Smart contracts are essentially computer code that executes business logic to automate the contractual terms between two parties.
Data Gumbo smart contracts are essentially computer code that executes business logic to automate the payment process between two parties upon contractual terms being met. Participating parties negotiate and agree on executable terms and conditions upfront, which then is written into lines of code. Both smart contract code and signed natural language agreements by participating parties are stored in a distributed and decentralized blockchain network.
Smart contracts utilize the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) connectivity to obtain necessary operations data to verify and ensure the predefined conditions are met. Once all required conditions are verified, smart contracts trigger automatic pre-reconciled payments. The frequency of payments is fully customizable as per the customer’s request, for example daily, weekly, monthly, or on a per transaction basis. IIoT data can be streamed from project execution tools, existing business management systems, project information management systems, sensors, GPS trackers, scanners, drones, and other common home office or field data sources prevalent in the industry.
.jpg?width=688&name=blockchain_as_service_animation3%20(1).jpg)
Why Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts powered by blockchain technology provide an innovative approach to streamline operations, improve visibility and transparency with accurate and current data, and empower counterparties to reduce inefficiencies and capture significant cost savings across the built environment.
Once a transaction is recorded on a blockchain, it is traceable, but not reversible or alterable. Thus, smart contracts permit trusted and transparent transactions and agreements to be carried out among parties without the need for a middleman, eliminating inefficiency and human errors along the process. Thanks to payment automation, contractors and suppliers get paid faster for services and products they delivered as per the agreement, thus freeing up working capital. It also means that owners/operators pay only for what actually is delivered or executed. As transactions are executed, all relevant data and documentation required to verify or audit consensus are posted to immutable blocks in a distributed ledger that is viewable to all involved parties.
As a neutral, third-party system, GumboNetTM creates a secure record of truth stored on a private, permissioned ledger system that leverages existing IT and data sources to digitally corroborate physical project events as they unfold in real-time. Blockchain enables a shared, single source of truth for all financial and technical transactional information across stakeholders. Beyond automating payments and decreasing Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) from the typical 60 to 120 days down to literally net one day, smart contracts eliminate manual and error-prone invoicing processes, minimize disputes and reconciliation burdens, and encourage higher productivity and quality.

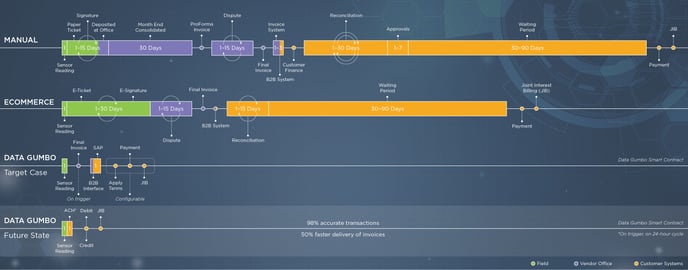
Data Gumbo’s smart contracts enable the transformation and modernization of industries from paper-based processes to a new digital operating model rooted in trust, collaboration, and cost efficiency.
